
These new regulations come as companies are antsy to get back into the office. In order to stay within the bounds of the law, companies only need to create alternative arrangements for those with legitimate medical and religious exemptions. It is closing its New York and San Francisco offices, and shelving any re-opening plans.Ĭompanies are legally allowed to mandate that employees get the vaccine in order to return to a physical office, guidance from the federal Equal Opportunity Employment Commission said in late May. Twitter, on the other hand, is taking a more conservative approach. Other companies also requiring vaccination are asset management firm BlackRock, investment bank Morgan Stanley, private hospital firm Ascension Health, ride-hailing company Lyft, and the casts and crews of Netflix shows. Google CEO Sundar Pichai says that the vaccine requirement will first be implemented in the United States, and later applied to its offices in more than 40 countries.

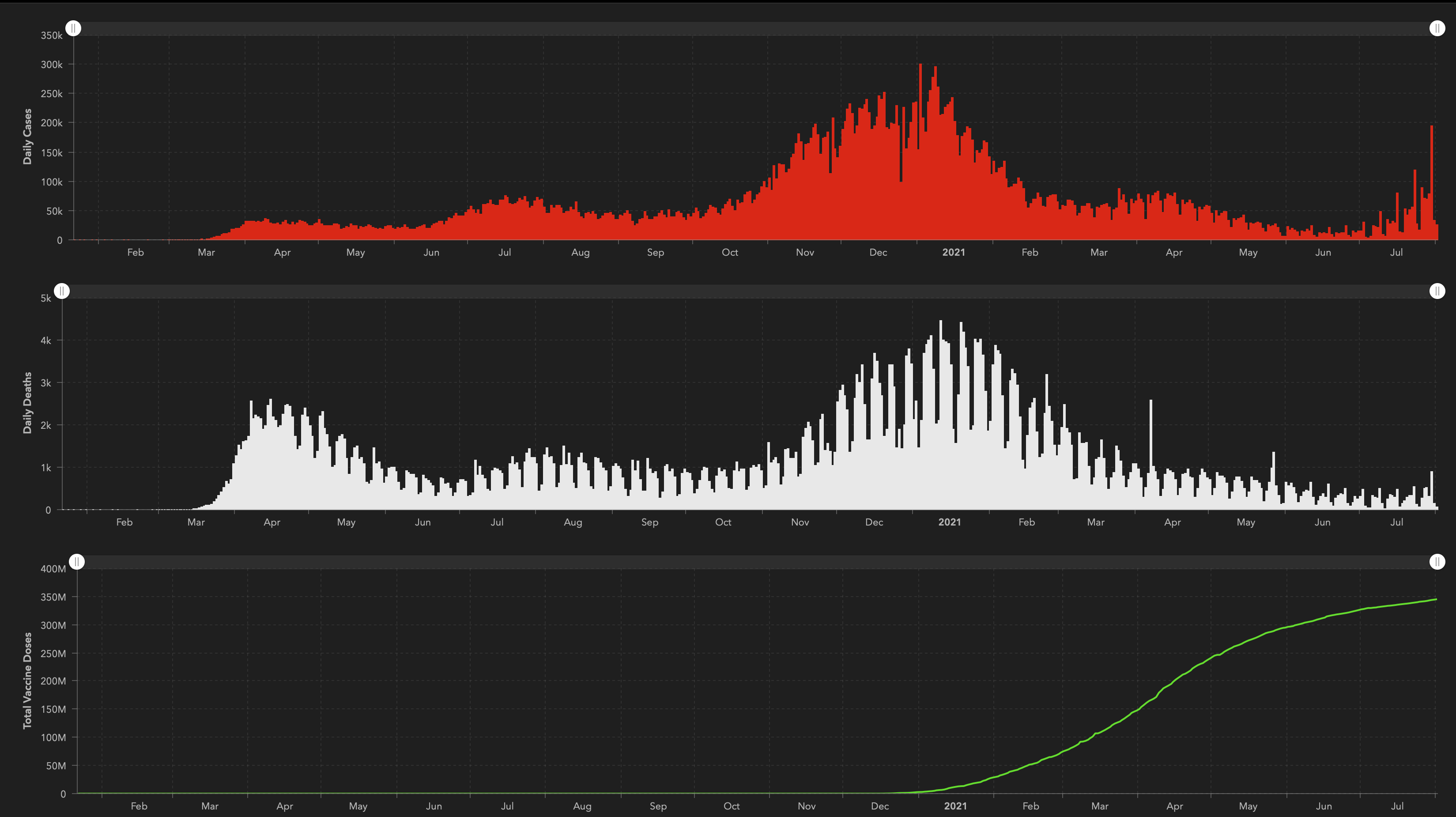
While the rapid development of vaccines against COVID‑19 is an extraordinary achievement, successfully vaccinating the global population presents many challenges, from production to distribution, deployment, and importantly, acceptance.This surge is emboldening tech companies like Google and Facebook, which took early precautions by closing offices in February and March 2020, to now require that employees are fully vaccinated before returning to work. Trust in the vaccines is vital, and is critically dependant on the ability of governments to communicate the benefits of vaccination, and to deliver the vaccines safely and effectively. This brief addresses the role of governments in promoting confidence in the effectiveness and safety through effective communication, as well as trust in their ability to procure and distribute them efficiently and equitably. While only a small minority of the population holds strong anti-vaccination views, hesitancy about COVID‑19 vaccination is evident in many countries. Recognising that vaccination campaigns of the magnitude needed are unprecedented, government actions to garner trust will be essential to their success, and to the emergence of more resilient societies after the crisis. While the development of COVID‑19 vaccines has been an extraordinary success, vaccinating most of the global population is an enormous challenge, one for which gaining – and maintaining – public trust in COVID‑19 vaccines and vaccination will be as essential as the effectiveness of the vaccines themselves.
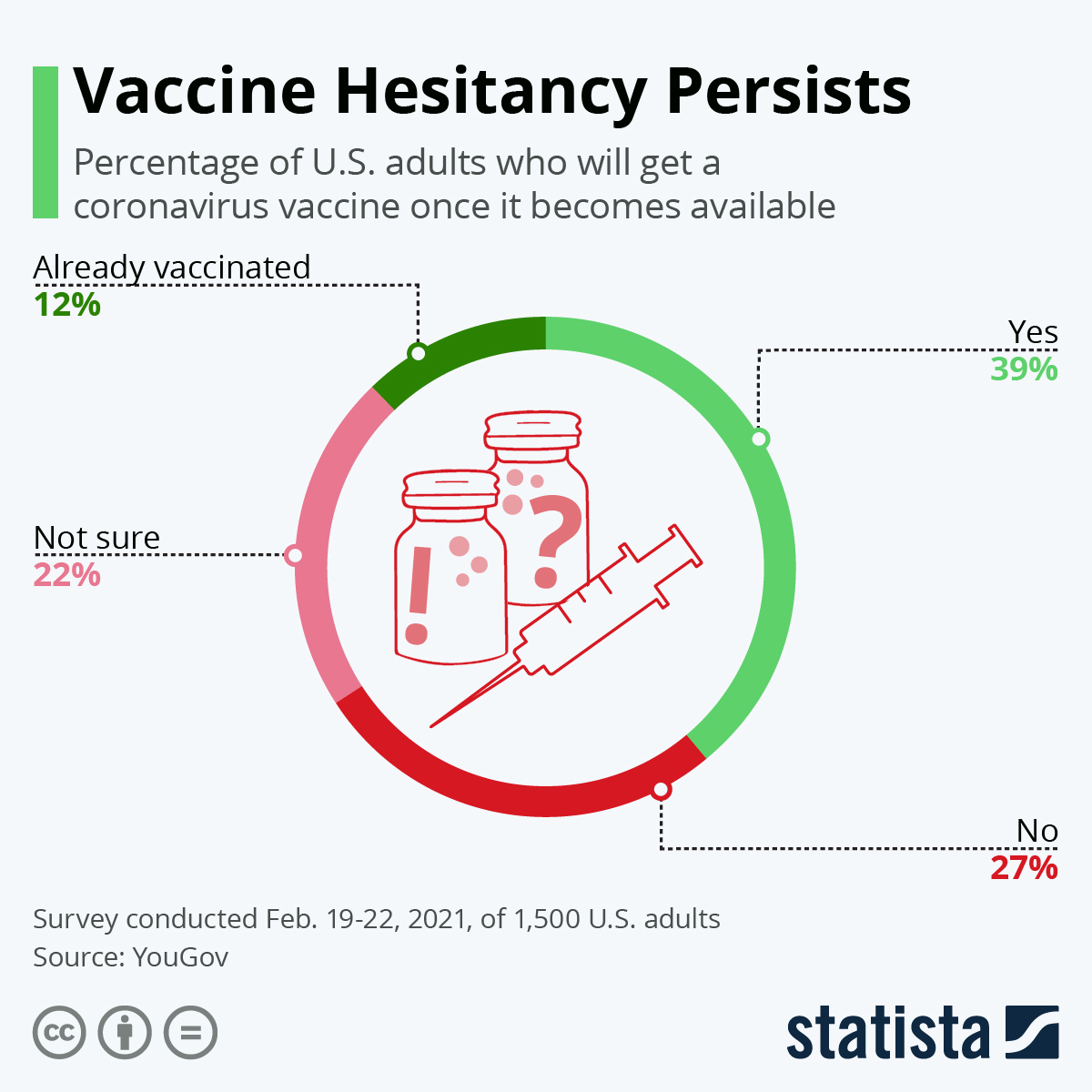
The capacity and effectiveness of regulatory agencies in handling issues and communicating consistently as events arise, while retaining public confidence in their review processes and The principles and processes that guide government decisions and actions in vaccine procurement, distribution, prioritisation, and administration The competence and reliability of the institutions that deliver them The extent to which the government can instil and maintain public confidence in the effectiveness and safety of the vaccines Trust in vaccination, and in the ability of governments to communicate, and to successfully deliver a vaccination programme, is critically dependent on: Moreover, the experience with COVID‑19 will likely shape confidence in other vaccines making it even more important to build confidence at this time. The effectiveness of the public engagement and communications that accompany these.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
